Table of Contents
Introduction
Are you experiencing unusual reactions after consuming potatoes? You may have a potato allergy, a rare but serious condition that can cause mild to severe symptoms. Understanding the triggers, symptoms, and safe food alternatives is crucial for managing this allergy effectively. This article provides a comprehensive guide on potato allergy, its symptoms, diagnosis, and the best ways to prevent reactions.
What is a Potato Allergy?
A potato allergy occurs when the immune system mistakenly identifies certain proteins in potatoes as harmful, leading to an allergic reaction. While more common in children, adults can also develop this allergy. Potato allergies can range from mild symptoms like itching to severe anaphylactic reactions requiring immediate medical attention.
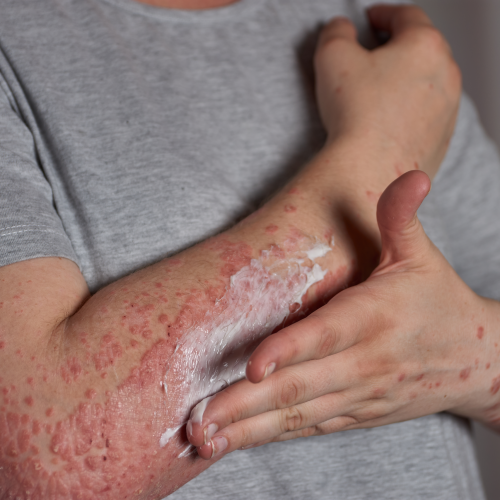
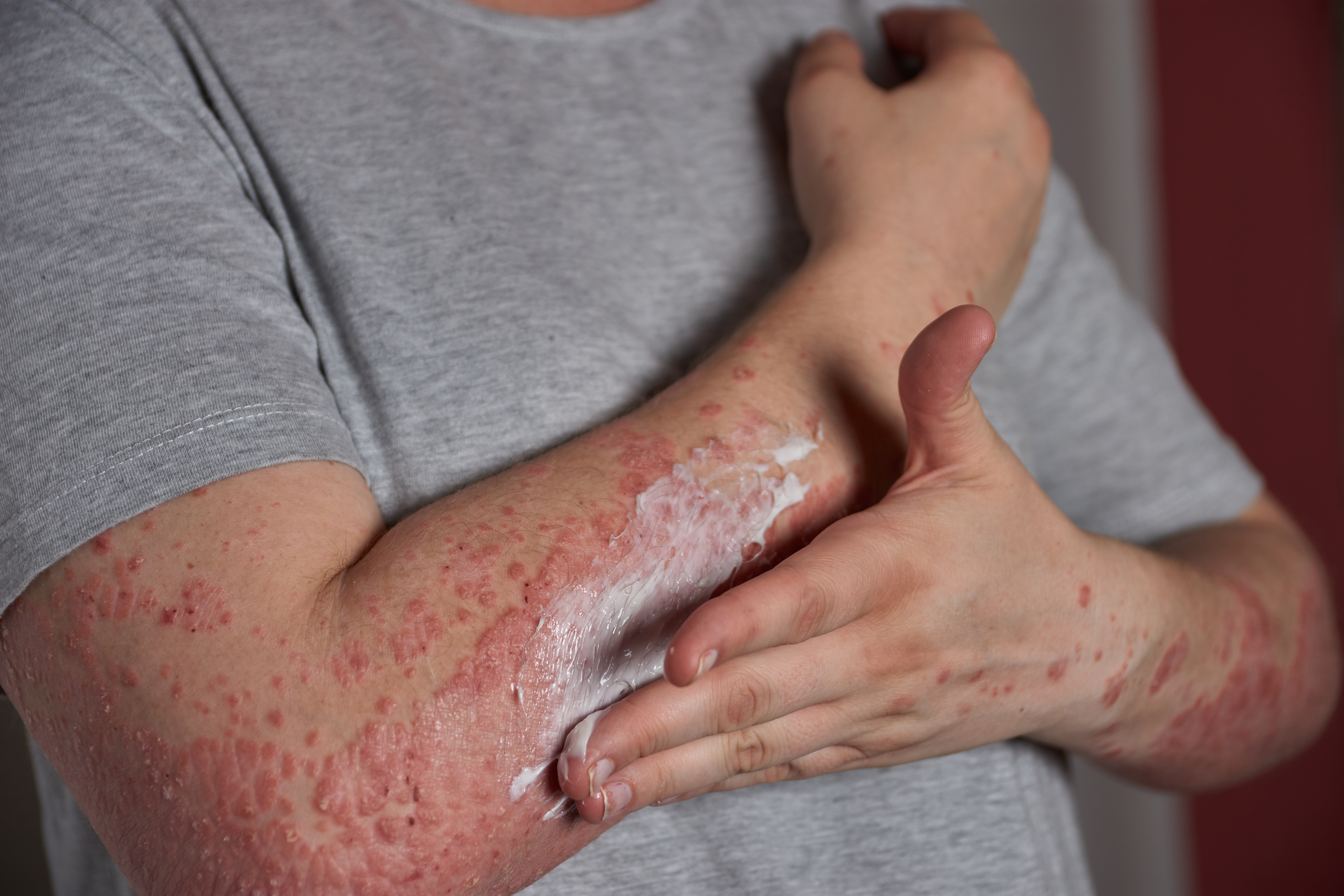
Symptoms of Potato Allergy
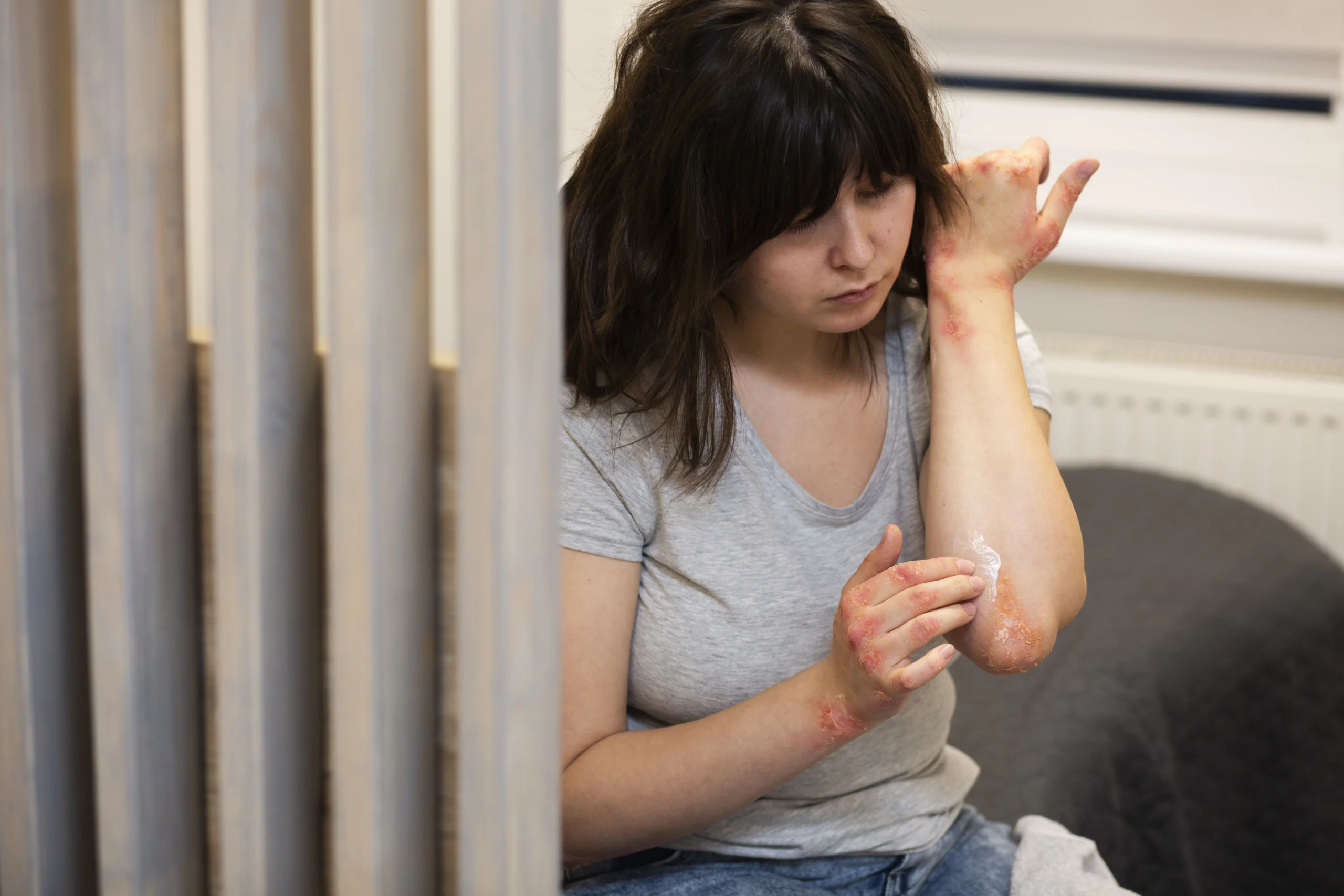
People with a potato allergy may experience various symptoms, which can occur within minutes or hours after consuming potatoes or potato-based products. Common symptoms include:
Common Symptoms of Potato Allergy
- Skin reactions (itching, hives, eczema)
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, or face
- Runny or congested nose
- Digestive issues (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea)
- Wheezing, coughing, or difficulty breathing
- Anaphylaxis (a severe reaction requiring immediate medical care)
Causes and Risk Factors
What Causes a Potato Allergy?
A potato allergy is caused by the body’s immune system overreacting to proteins in potatoes, such as patatin. Some individuals may be more sensitive to raw potatoes than cooked ones due to changes in protein structures when heated.
Who is at Risk?
- Individuals with a family history of food allergies
- Those allergic to similar foods like tomatoes, eggplants, and bell peppers
- People with pollen allergies, as potato proteins can cross-react with certain pollens
Diagnosis and Testing
If you suspect a potato allergy, consult an allergist for proper diagnosis. The following tests may be conducted:
How is a Potato Allergy Diagnosed?
- Skin Prick Test: A small amount of potato extract is applied to the skin to observe reactions.
- Blood Test: Measures the presence of specific IgE antibodies linked to potato allergy.
- Oral Food Challenge: Conducted under medical supervision to confirm allergic reactions.
Managing a Potato Allergy
Avoiding potatoes and potato-based products is the best way to prevent allergic reactions. However, hidden potato ingredients in processed foods require careful label reading.
Safe Foods and Alternatives
If you have a potato allergy, here are some safe alternatives:
- Grains: Rice, quinoa, and oats
- Vegetables: Carrots, sweet potatoes, and zucchini
- Flour Substitutes: Almond flour, coconut flour, and chickpea flour
- Snacks: Corn chips, gluten-free crackers, and rice cakes
Foods to Avoid
- Potato chips and fries
- Mashed potatoes and baked potatoes
- Soups and stews containing potatoes
- Processed foods with potato starch or modified food starch
Treatment Options
How to Treat a Potato Allergy Reaction
- Antihistamines can help relieve mild symptoms like itching or hives.
- Epinephrine (EpiPen) is necessary for severe reactions like anaphylaxis.
- Avoidance is the best preventive measure to manage a potato allergy.
Considerations Before Consuming Any New Food
Before eating new foods, always check ingredient labels for hidden potato derivatives. When dining out, inform restaurant staff about your allergy to prevent cross-contamination.
See Also: What is Silicone Allergy?
Conclusion
A potato allergy can be challenging to manage, but with the right precautions, you can maintain a safe and balanced diet. Identifying symptoms, undergoing proper testing, and avoiding potato-based foods will help prevent allergic reactions. If you suspect a potato allergy, consult an allergist for a personalized management plan. By staying informed and cautious, you can lead a healthy, reaction-free life!